Sustainability, especially in such a high emission sector, is a top priority for the longevity of the business. Here are five ways manufacturers can reduce their emissions.
Submetering
What is a submetre?
Building metres measure the energy delivered from the utility into your building or facility. Many buildings have multiple building metres. A submetre is a metre within your building or facility for specific energy measurements.
Submetering is when a metre – BTU, electric, gas, steam, or water metre – is used within a building or facility to measure the amount of energy for a specific purpose or area.
For example, in a chilled water plant, submetering uses BTU metres with electric metres to measure a specific chill water pump’s efficiency.
What types of submetering are there?
Several subcategories fall under the submetering umbrella.
Tenant submetering is a subcategory that focuses on measuring tenant-specific energy use, which may include demand measurements.
Plant submetering, most relevant to manufacturers, uses submetres to measure your plant’s energy. Submetres may include BTU metres, electric metres, flow metres, gas metres, steam metres, and metres embedded in your plant management systems.
The Benefits of Submetering
For organisations with high energy consumption, implementing a sub-metering system can assist you in identifying areas of inefficiency. It can also be used to educate and inform staff of (more) individual usage.
In doing this, you make it easier for behavioural changes to take place across the business and you increase the likelihood of enhancing your business energy efficiency.
In fact, implementing submetering technologies can help you reduce energy use by up to 16%.
What’s more, submetered data may help to identify problems with equipment. Addressing those problems may not only save energy, but prolong the life of the equipment or identify a piece of equipment that is failing
Submetering Monitoring
Any metre installed for billing purposes must be one which is approved by Ofgem or MID.
If you are thinking of installing sub-metres in your property, make sure you’re aware of the below checklist:
- Ensure the metres are Ofgem/MID approved
- Read and inspect metres every two years
- Check metres are in good working order regularly
- Adhere to the RICS Code of Practice when you’re charging tenants for energy
Installation must be carried out by qualified electricians.
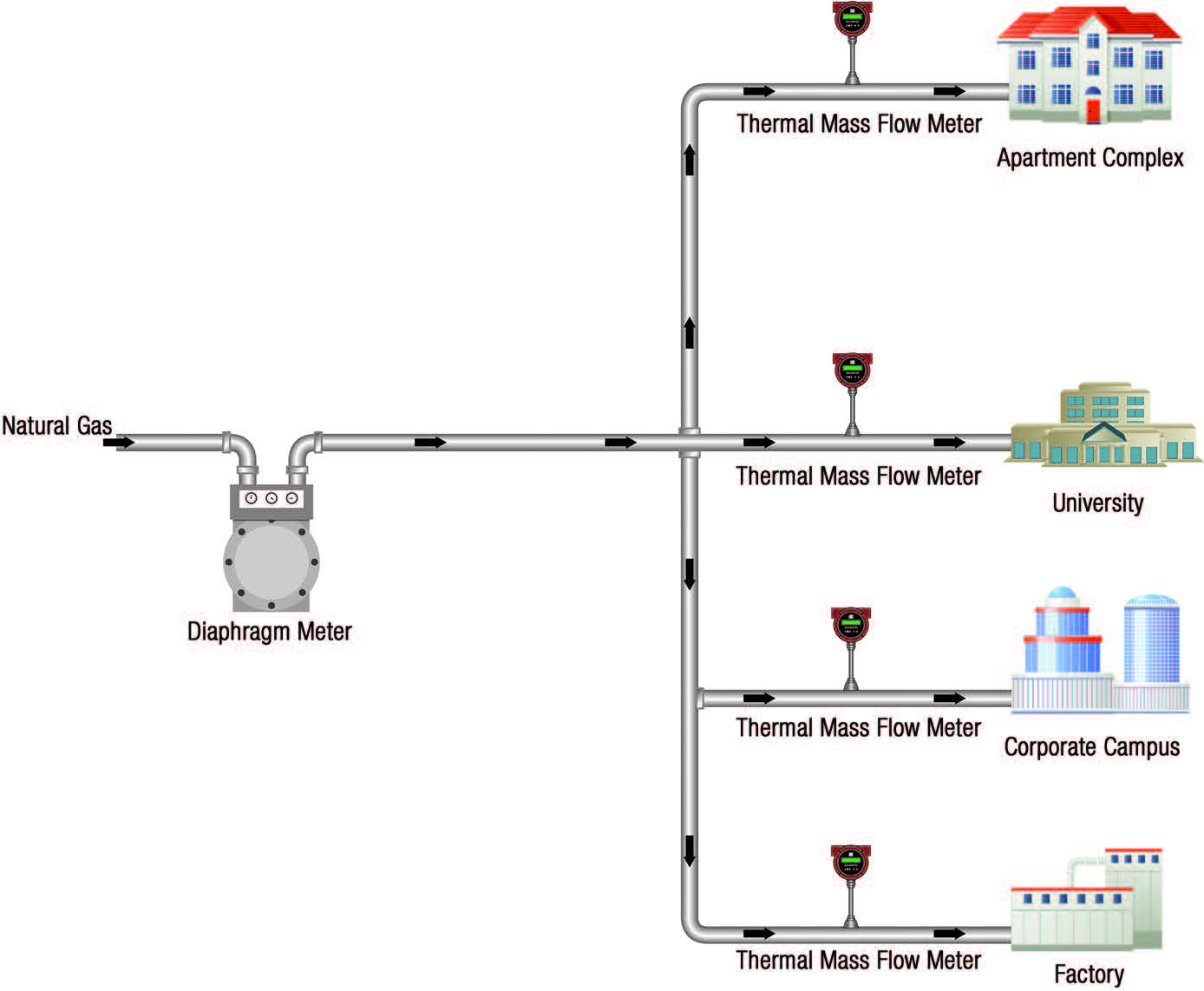
Submetres will be fitted to key machines or sites from the main metre, giving you more accurate data to make data saving decisions.
Source: sierrainstruments
Base Load Analysis
In buildings, base load refers to the consumption of electricity, gas and water that is not related to productive activity. It’s the amount of resources that a facility consumes around the clock, even when no one is working. Historically, base load has been accepted as a ‘fixed’ cost, but there’s actually a lot of waste that could be trimmed and turned into savings.
What’s changed?
Enhanced data management often reveals a host of hidden savings opportunities in manufacturing environments. In fact, reducing base-load can yield 5% or more in annual energy savings and GHG reductions through simple operational changes such as control adjustments or maintenance to address equipment wear-and-tear.
Saving money with Base Load Analysis
Once you have the data, here are three key steps for base-load analysis.
- Analyse electricity, gas and water usage data against a measure of plant production (hourly is best, by shift or day if limited by available data)
- Estimate the magnitude of your fixed/base load and calculate the annual cost of this energy
- Investigate and understand the components of fixed load (i.e., specific loads)
Convenience vs. productivity
When assessing the base load of manufacturing facilities, it’s important to make the distinction between convenience operation and productive operation. A facility may operate 24 hours per day, seven days per week, but how many of those hours is the plant operating at maximum capacity versus sitting idle? Which specific loads are on during non-working hours and are they truly necessary?
Just as a plant would not schedule large numbers of employees that sit idle during times of low productivity, or expect to consume raw materials during such times, energy and water consumption should be managed to the minimum required for safe and effective plant operations.
For example, advancements in building and process efficiency over time could lead to existing electrical power distribution systems that are oversized for the present-day load.
In this case, a significant proportion of what is presumed to be fixed cost could turn out to be waste. Doing a base load analysis gives visibility over energy use and provides opportunity for energy efficiency.
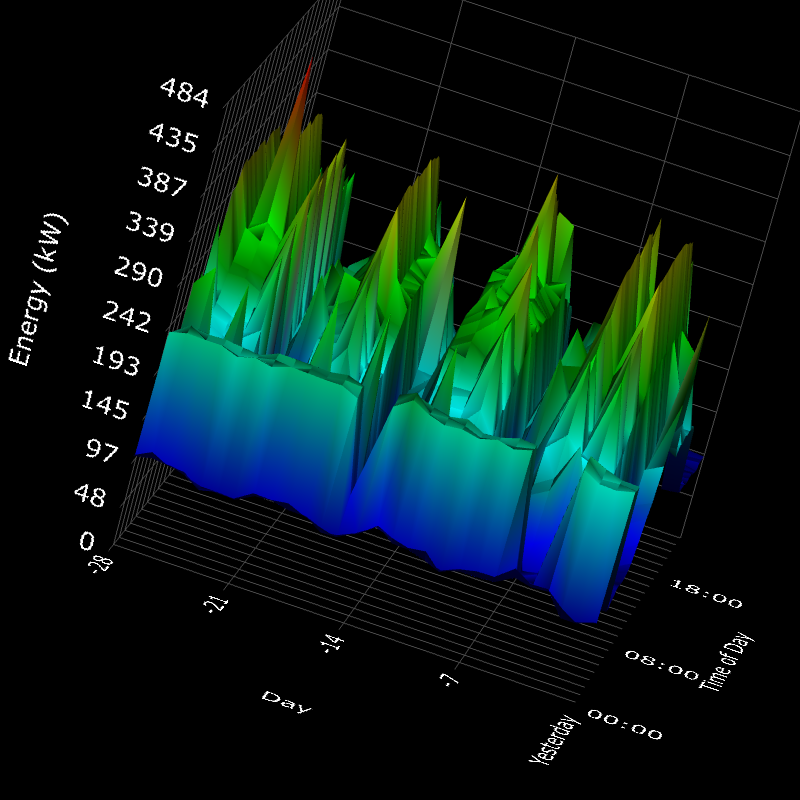
This graph containing mock data shows the energy usage (xz plane) from today back in time through the previous 28 days (yz plane), as well as throughout the day (xy plane). This gives full visibility over when energy is being used exactly when so you can work out where to improve energy efficiency and save money. If you have a smart meter, you will be able to view this on your account in the Enistic Platform.
Source: the Enistic Platform
Heat pumps
What is a heat pump?
An air source heat pump transfers heat from the outside air to water, which heats your rooms via radiators or underfloor heating. It can also heat water stored in a hot water cylinder for your hot taps, showers and baths.
Heat from the air is absorbed into a fluid. This fluid then passes through a heat exchanger into the heat pump, which raises the temperature and then transfers that heat to water.
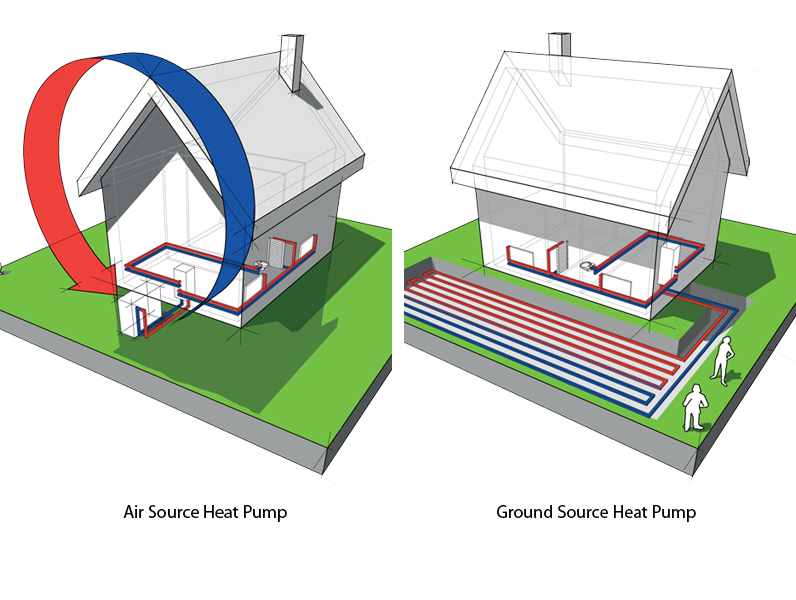
Source: greensquare.co.uk
A ground source heat pump transfers heat from the ground outside your home to heat your radiators or underfloor heating. It can also heat water stored in a hot water cylinder for your hot taps and showers.
Benefits of heat pumps
Despite the initial cost of installing a heat pump system there are significant savings that can be made on your fuel bills if you are currently using electricity, oil, solid fuel or liquid gas to heat your premises.
You will also be able to benefit from the new Boiler Upgrade Scheme) which offers you money off the installation of heat pumps and it shouldn’t need any regular maintenance and could last between 10 and 25 years or more.
Heat pumps improve air quality, have low noise, low running costs, and can be used as air conditioning, cooling down the office environment when needed, and providing a controlled climate.
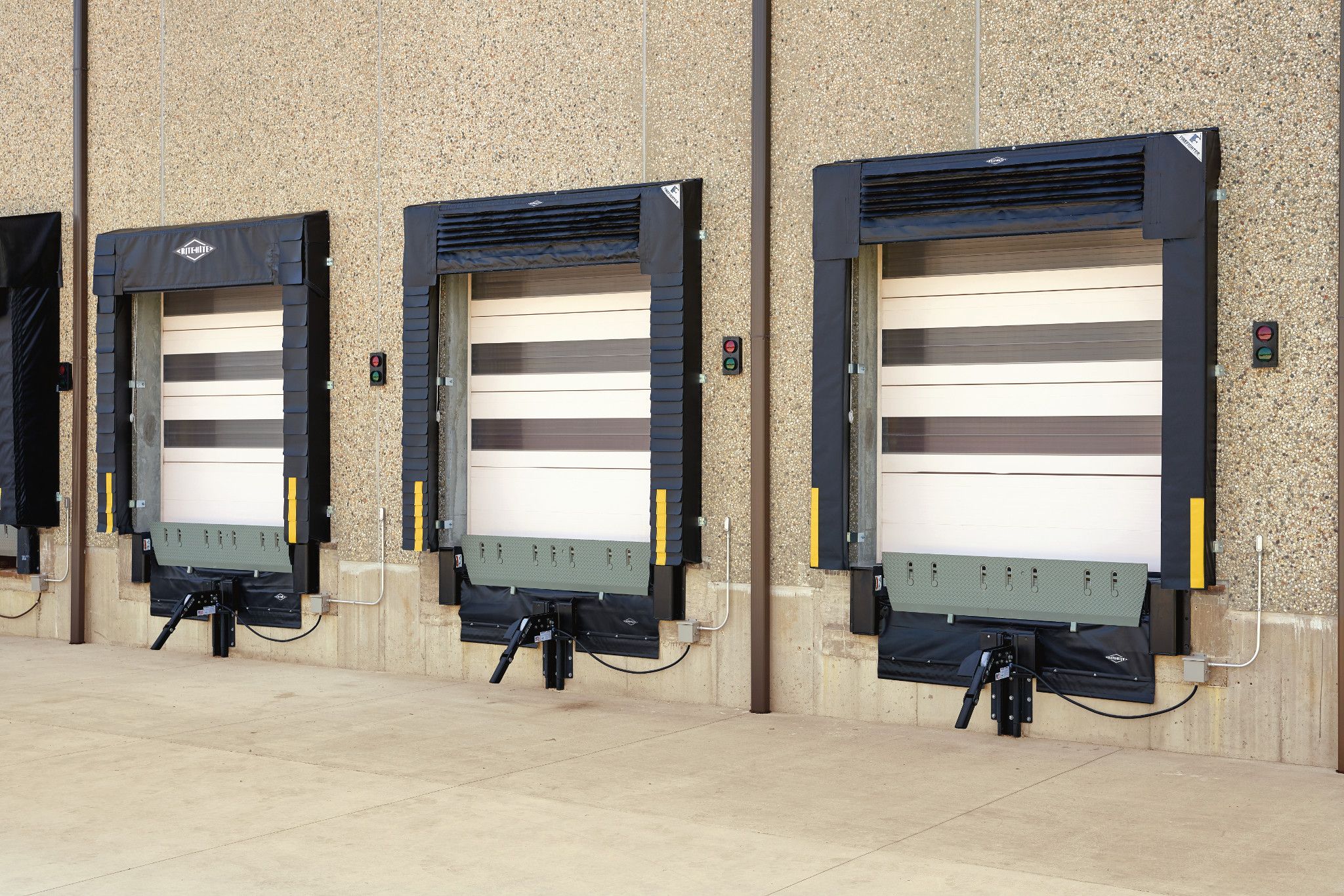
Effective docking seals
It may seem like a small issue, but each little gap you see around a parked vehicle at a loading dock is costing you money each and every day.
The heating and air conditioning that escapes through these gaps can cost you hundreds of pounds per year, per dock position. Those gaps also allow unwanted outside elements like dust, wind, rain, bugs and rodents into your facility. This can easily contribute to product damage, cause issues with warehouse inspections, and create an uncomfortable environment for your employees to work in.
Seals vs shelters
The primary difference between loading dock seals and loading dock shelters is that loading dock seals do not extend very far away from the loading dock entrance and instead form a seal where the trailer edge is about to meet the loading bay edge. These are adept at controlling the climate because they make a tunnel between the loading bay and the trailer of a truck.
Loading dock shelters, on the other hand, extend a little bit further away from the receiving bay and extend all the way around to form a miniature tunnel between the bay and the truck’s trailer.
Loading dock seals are slightly better at climate control because they form a tight seal between the trailer and the loading dock door.
Benefits
Although installing them is an extra cost, dock seals and shelters can quickly pay for themselves through reduced heating and cooling costs within your facility. Protecting your dock area from wet weather makes your dock a much safer place and sealing your doors increases worker comfort, morale and productivity.
As well as protecting against harmful weather, dock seals minimise the entry of vermin such as rats and helps prevent unauthorised entry into your facility, making them safer for your health and safety.
Using efficient docking seals means that docked trailers can become secure, climate controlled extensions of your facility.

Destratification fans
The use of destratification fans in industrial buildings with high ceilings, operating a warm air heating system, can reduce energy consumption by 20%.
Every building will experience some degree of thermal stratification, a natural process that causes warm air rises to the ceiling or roof space and displaces cooler air, pushing it downwards into the occupied space. In most workspaces, irrespective of the height of the ceiling, the occupied space where people need to be kept warm is up to around 2m from the floor. Any energy used to heat the air above this point is therefore generally wasteful.
A simple but highly effective solution is to use destratification fans working in harmony with a warm air heating system to return the warm air from the roof space back to the occupied space.
How they work
Destratification fans reverse the natural convection process, recirculating warm air back to working level.
In any space, heat naturally rises to ceiling level, making it more difficult to warm high ceilinged areas at occupancy level. Destratification fans are designed to recirculate this warm air, as it rises back to the desired level.
The Benefits Of Destratification Heating
A well-designed destratification system addresses all of these issues by ensuring effective distribution of heat throughout the space so that stratification is minimised and there is only a very small temperature gradient between the working zone and the roof space. The ability of the destratification system to reduce the temperature of the air in the roof space also reduces the rate of heat loss through the roof. For example, if the roof space temperature were reduced from 24°C to 20.5°C this would result in around a 14% reduction in the heat loss through the roof membrane. In many cases improving the distribution of warm air with destratification will make it possible to maintain the required temperature in the working zone with fewer warm air heaters, thereby reducing both capital and running costs. In industrial buildings, the destratification fans will also recirculate the heat from machinery, so that less energy is consumed by the heating system.
Furthermore, improved air distribution helps to eliminate hot and cold spots in the working zone to improve comfort levels. Destratification fans can also be used to provide cooling draughts of air during the summer.
Find out more about how we can help manufacturers!

The Enistic Platform
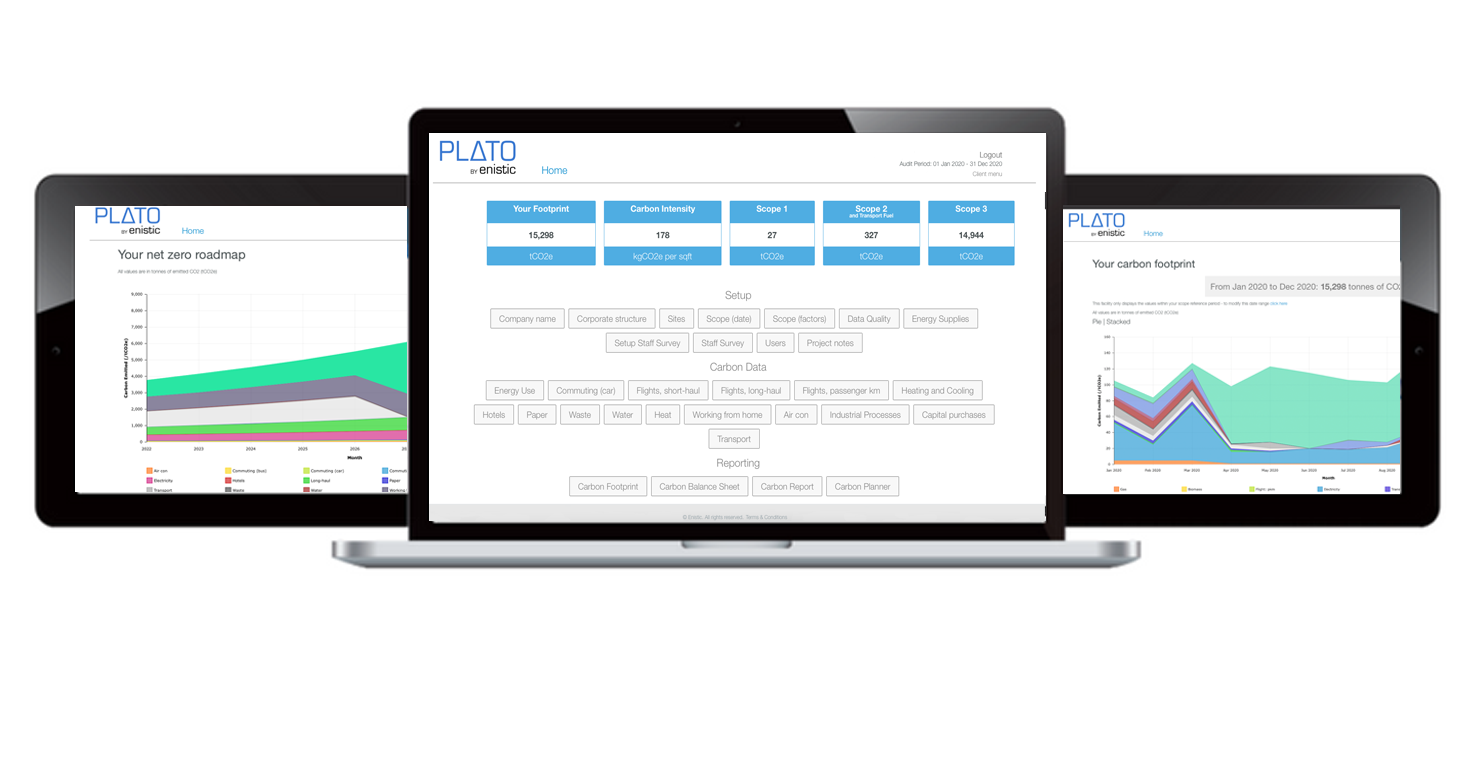
Our cloud-based carbon management platform pulls together your carbon data into one, easy-to-access place. Intuitive dashboards help you to visualise key metrics, and monitor performance at a glance. The built in analytics suite enables you to create customisable reports that can be exported and shared with your organisation. Download reports and share your carbon data and progress easily.
• Live carbon Footprint Trace
• Report your progress to stakeholders
• Up-to-date conversion factor
• Analyse and compare individual sites
• Contact Enistic’s experts for specialist support
• Downloadable and customisable reports
Book a free consultation
Contact one of our Net-Zero experts today and book a free consultation to see how Enistic can help you set your Net Zero strategy. We will make the processing time and cost-effective. ensuring you move forward, informed, empowered, and confident that you have control.




